Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-04-18 Origin: Site











In the realm of plastic injection molding, understanding the intricacies between single-cavity and multi-cavity molds is paramount for manufacturers aiming to optimize production efficiency and product quality. These molds serve as the backbone of mass production in various industries, from automotive to consumer goods. While both types of molds are employed to produce identical or similar components, they differ significantly in design, cost, production speed, and application. This article delves deep into the distinctions between single-cavity and multi-cavity molds, providing a comprehensive analysis that encompasses technical specifications, economic considerations, and practical applications. By exploring these differences, manufacturers can make informed decisions that align with their production goals and operational capacities. For expert insights on high-quality molds, consider exploring our offerings on Commodity Mould.
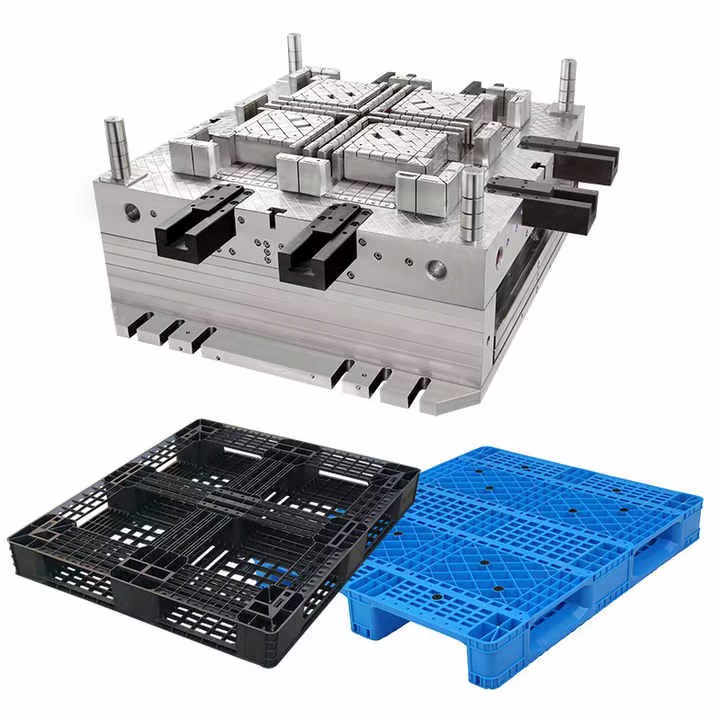
Injection molding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mold. It's widely used for fabricating items from plastic trinkets to complex automotive components. The molds used in this process are critical, as they define the shape and surface finish of the final product. Understanding the fundamental mechanics of injection molding provides a foundation for appreciating the nuances between single-cavity and multi-cavity molds.
The process involves heating plastic pellets until they become molten and then injecting this molten plastic under high pressure into a mold cavity. After cooling and solidification, the part is ejected. This cycle repeats for mass production. The efficiency and quality of this process heavily depend on the design and type of mold used.
Single-cavity molds are designed to produce one part per injection cycle. They're simpler in design and are often used for low-volume production or products that require exceptional precision. The initial investment is generally lower compared to multi-cavity molds, making them suitable for startups or specialized productions.
Reduced upfront tooling cost.
Simpler mold design leading to shorter manufacturing lead times.
Easier maintenance and lower risk of defects per cycle.
Greater control over individual part quality.
Slower production rates due to one part per cycle.
Higher per-unit cost when scaling up production.
Not ideal for meeting high-volume demands promptly.
Multi-cavity molds feature multiple cavities within a single mold, allowing for the production of several parts per injection cycle. They're engineered for high-volume manufacturing, significantly increasing production efficiency. The cavities can be identical, producing multiple copies of the same part, or family molds producing different parts in one cycle.
Increased production output, reducing lead times.
Lower per-unit cost due to economies of scale.
Efficient use of injection molding machines.
Ideal for meeting large market demands quickly.
Higher initial tooling costs and complexity.
Increased potential for variability between cavities.
More complex maintenance and longer setup times.
Requires more powerful injection molding machines.
The primary technical distinction lies in the mold design and the number of cavities. Single-cavity molds have one cavity, while multi-cavity molds contain multiple cavities, sometimes up to 128 or more. This difference impacts the mold's size, the injection molding machine's requirements, and the overall production process.
Single-cavity molds are straightforward, making them easier to design, manufacture, and maintain. Multi-cavity molds require precise engineering to ensure uniform filling, pressure, and cooling across all cavities. This complexity demands advanced technology and expertise in mold manufacturing.
Multi-cavity molds require machines with higher clamping force and injection capacity to accommodate the increased number of cavities. This requirement may lead to additional investment in machinery. In contrast, single-cavity molds can operate on smaller, less expensive machines.
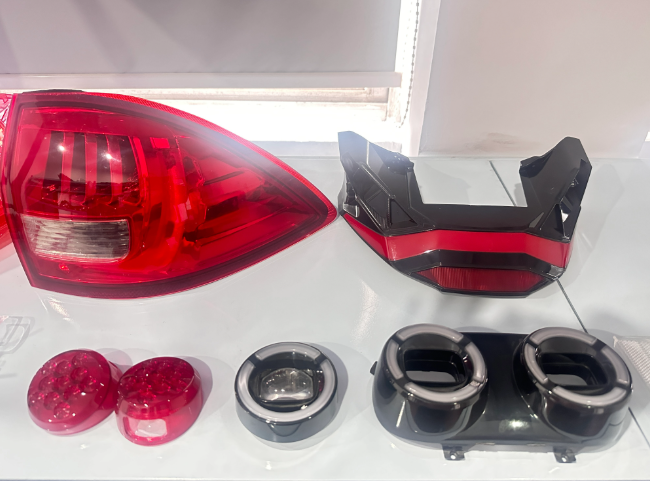

From an economic perspective, the choice between single-cavity and multi-cavity molds hinges on factors like production volume, budget, and cost per part. Manufacturers must analyze these aspects to determine the most cost-effective option for their specific needs.
| Aspect | Single-Cavity Mold | Multi-Cavity Mold |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Tooling Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Production Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Per Unit Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Maintenance Costs | Lower | Higher |
Conducting a break-even analysis helps determine at what production volume the investment in a multi-cavity mold becomes more cost-effective than a single-cavity mold. Generally, higher volumes favor multi-cavity molds due to reduced per-unit costs, despite the higher initial investment.
Quality control is a critical aspect of injection molding. The mold type influences the consistency and quality of the produced parts. Single-cavity molds offer better control over each part, reducing the risk of variability. Multi-cavity molds may introduce inconsistencies if not precisely engineered and maintained.
In multi-cavity molds, ensuring that all cavities fill uniformly is essential. Variations in temperature, pressure, or mold design can result in discrepancies between parts. Advanced simulation software and mold flow analysis are often employed to mitigate these risks.
Defects in single-cavity molds impact only one part per cycle, making them easier to isolate and address. In multi-cavity molds, a defect in the mold can affect multiple parts simultaneously, potentially increasing waste and requiring more extensive quality assurance measures.
Choosing between single-cavity and multi-cavity molds depends on the specific application and production requirements. Factors such as product complexity, required precision, anticipated production volume, and budget constraints play pivotal roles in this decision.
Low-volume production runs.
High-precision parts requiring stringent quality control.
Prototyping and product development phases.
Budget limitations on initial tooling costs.
High-volume production demands.
Reduced per-unit manufacturing costs.
Products with less stringent individual part precision.
Established products with consistent demand.
Advancements in technology have blurred the lines between the limitations of single-cavity and multi-cavity molds. Enhanced manufacturing techniques and materials have improved the performance and feasibility of both mold types in various applications.
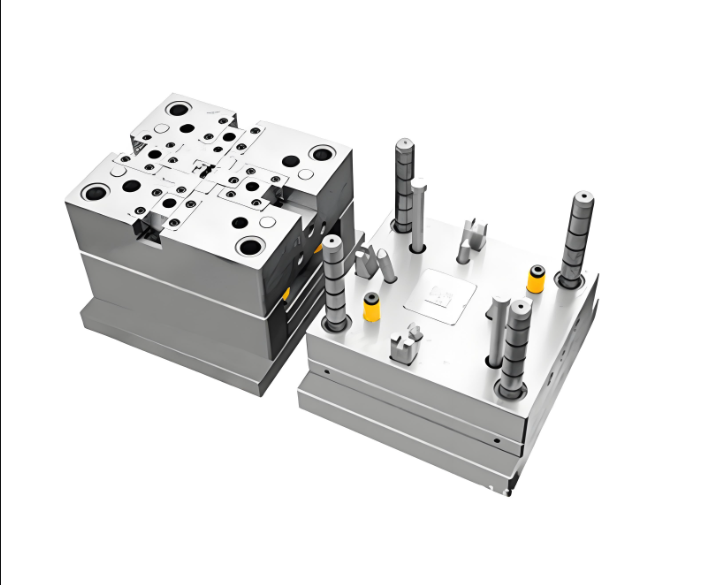

Hot runner systems maintain the plastic in a molten state within the mold, reducing waste and improving cycle times. They're particularly beneficial in multi-cavity molds, enhancing efficiency and part quality.
Utilizing advanced materials like hardened steel or aluminum alloys can extend mold life and improve thermal conductivity. These materials can be tailored to suit the specific needs of single-cavity or multi-cavity molds.
Examining real-world scenarios where manufacturers chose one mold type over the other provides practical insights into the decision-making process and outcomes.
A medical device company required highly precise components with strict regulatory compliance. Opting for single-cavity molds ensured each part met exact specifications, resulting in zero defects and full compliance with industry standards.
A consumer goods manufacturer needed to produce millions of plastic caps for beverage bottles. Utilizing a 64-cavity mold drastically reduced production time and costs, enabling the company to meet market demand efficiently.
Sustainability is increasingly important in manufacturing. The choice of mold type can impact energy consumption, material waste, and overall environmental footprint.
Multi-cavity molds with hot runner systems reduce material waste by eliminating runners and sprues that solidify and become scrap. This efficiency contributes to lower raw material consumption and waste generation.
Producing multiple parts per cycle in multi-cavity molds can reduce the energy consumed per part. However, the larger machines required may offset some of these savings. Single-cavity molds use smaller machines but produce fewer parts, affecting overall energy efficiency.
The injection molding industry continually evolves with advancements in technology and changing market demands. Understanding future trends helps manufacturers stay competitive and make forward-thinking decisions regarding mold selection.
Increased automation in injection molding processes enhances efficiency and consistency. Smart factories utilize data analytics and machine learning to optimize production, making both single-cavity and multi-cavity molds more effective in different scenarios.
The demand for customized products and shorter product life cycles encourages the use of single-cavity molds for rapid prototyping. Additive manufacturing technologies, like 3D printing, complement traditional injection molding, providing flexibility in design and production.
Selecting between single-cavity and multi-cavity molds is a critical decision that impacts production efficiency, cost, and product quality. Single-cavity molds offer simplicity, precision, and lower initial costs, suitable for low-volume or high-precision manufacturing. Multi-cavity molds provide higher output and lower per-unit costs, ideal for large-scale production. Manufacturers must consider their specific needs, resources, and market demands when making this choice. By understanding the differences and evaluating the advantages and limitations of each mold type, businesses can optimize their manufacturing processes. For high-quality mold solutions tailored to diverse industrial needs, explore our durable Commodity Mould offerings.
