Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-06-13 Origin: Site











Moulds play a significant role in various industries, especially in the medical sector where precision and safety are paramount. Understanding the terminology and applications of moulds in medicine is essential for professionals involved in healthcare manufacturing and supply. This article delves into the medical term for mould and explores its implications in the medical field, providing a comprehensive overview for those interested in the intricacies of medical mould technology. Companies specializing in Medical Mould manufacturing are at the forefront of this innovative field.
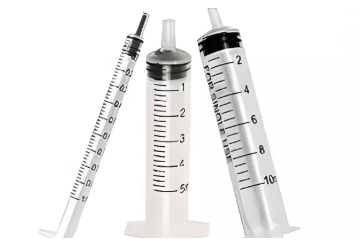
In the context of healthcare, the term "medical mould" refers to precision-engineered tools used for creating medical devices and components through the process of injection moulding. These moulds are critical in producing a wide array of medical products such as syringes, tubing connectors, implantable devices, and diagnostic equipment components. The accuracy and quality of the mould directly impact the performance and safety of the medical devices produced.
Medically, the term "mould" is often associated with fungi that can cause health issues, but in manufacturing, it denotes the cavity or matrix used to shape materials. The medical term for mould in the manufacturing sense doesn't differ from the general term; however, it's crucial to distinguish between "mould" as a fungus and "mould" as a shaping tool in medical device production. In the United States, the spelling "mold" is commonly used, while "mould" is used in British English.
Medical moulds are essential in producing high-precision components required for modern medical devices. The stringent requirements of the medical industry demand that these moulds meet exact specifications to ensure patient safety and device efficacy. Advanced mould manufacturing techniques enable the production of complex geometries with tight tolerances, a necessity for components like microfluidic devices and minimally invasive surgical tools.
The materials used in medical moulding are typically medical-grade polymers that offer biocompatibility, sterilizability, and mechanical properties suitable for medical applications. Common materials include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), polycarbonate (PC), and thermoplastic elastomers (TPE). The selection of material depends on the device's intended use, required durability, and compatibility with bodily tissues and fluids.
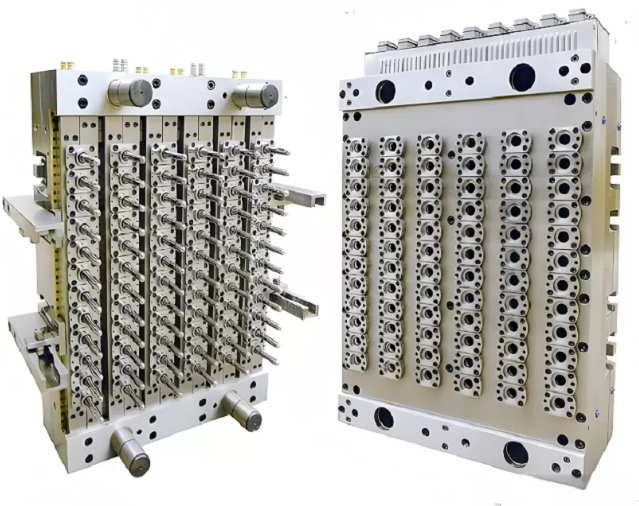
Injection moulding is a prevalent method in medical device manufacturing due to its efficiency and ability to produce complex parts at high volumes with consistent quality. The process involves melting medical-grade plastic pellets and injecting them into a mould cavity where the material cools and solidifies into the desired shape. This technique is ideal for producing components with intricate designs and tight tolerances, crucial for medical applications.
Quality control in medical moulding is critical. Manufacturers must adhere to strict regulatory standards such as ISO 13485, which specifies requirements for a quality management system to demonstrate the ability to provide medical devices and related services consistently. Rigorous testing and validation processes ensure that each component meets the necessary specifications and is safe for medical use.
Advancements in technology have led to significant innovations in medical moulding. Incorporating automation and robotics in mould manufacturing enhances precision and reduces production time. Additionally, the integration of computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) allows for more complex and accurate mould designs, facilitating the production of sophisticated medical devices.
Micro-moulding is a specialized form of injection moulding that produces extremely small and precise components, often with features measured in micrometers. This technology is vital for manufacturing miniature medical devices such as implantable sensors, microneedles, and components for minimally invasive surgical instruments. The demand for smaller, less invasive medical devices drives the growth of micro-moulding in the medical industry.
Manufacturing medical moulds presents several challenges. The need for absolute precision requires high-end equipment and expertise. Material selection is critical, as the mould must withstand high temperatures and pressures during the injection process without compromising integrity. Additionally, maintaining cleanliness to prevent contamination is essential, given the moulds' application in producing medical devices.
Compliance with regulatory standards is a significant challenge. Manufacturers must navigate a complex landscape of regulations imposed by agencies such as the FDA in the United States and the EMA in Europe. These regulations ensure that all medical devices are safe and effective, requiring comprehensive documentation and validation of manufacturing processes.
Selecting a reliable Medical Mould supplier is crucial for success. An experienced manufacturer brings expertise in design, material selection, and process optimization. They can assist in navigating regulatory requirements and ensure that the final product meets all necessary standards. Collaboration with the right partner can streamline production and enhance product quality.
When choosing a medical mould manufacturer, consider their track record, technical capabilities, quality assurance processes, and familiarity with regulatory compliance. It's essential to assess their ability to produce high-precision moulds and their commitment to maintaining stringent quality control throughout the manufacturing process.
Examining real-world applications provides insight into the impact of medical moulding technology. For instance, the development of custom moulds for insulin pens has enabled the mass production of reliable and easy-to-use devices for diabetes management. Similarly, moulds designed for producing components of minimally invasive surgical instruments have advanced the capabilities of surgeons and improved patient outcomes.
Medical moulding has revolutionized the field of prosthetics by allowing for the creation of custom-fitted components that enhance comfort and functionality for the user. Advanced moulding techniques enable the production of prosthetic limbs with integrated sensors and actuators, improving the wearer's control and interaction with the environment.
Looking ahead, the medical moulding industry continues to evolve with emerging technologies such as additive manufacturing (3D printing) and smart materials. These advancements hold the promise of creating more complex and patient-specific medical devices. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in the manufacturing process can lead to improvements in efficiency and quality control.
There is a growing emphasis on sustainability in medical manufacturing. Developing eco-friendly materials and processes in medical moulding not only reduces environmental impact but can also lead to cost savings. Manufacturers are exploring biodegradable polymers and recycling initiatives to minimize waste and promote environmental stewardship.
Medical moulds are integral to the production of high-quality medical devices that improve patient care and treatment outcomes. Understanding the medical term for mould and its significance in device manufacturing is crucial for professionals in the healthcare industry. As technology advances, the capabilities of medical moulding continue to expand, offering exciting possibilities for innovation. Partnering with a reputable Medical Mould ensures access to the latest technologies and expertise, paving the way for the development of cutting-edge medical solutions.
